front-door
So we are given a web, which can be logged in temporarily, and we can login with anything but not admin,

After login, u will notice that there is JWT cookie,
eyJhbGciOiAiQURNSU5IQVNIIiwgInR5cCI6ICJKV1QifQ.eyJ1c2VybmFtZSI6ICJiYXIiLCAicGFzc3dvcmQiOiAiYmFyIiwgImFkbWluIjogImZhbHNlIn0.JZOAYHBBBBNBDDQABXBFJOABZBLBBSOBVLBWVBQRSJJBOJYXDQZBEIRQBSOOFFWB
and if u access /products, there is some functions
def has(inp):
hashed = ""
key = jwt_key
for i in range(64):
hashed = hashed + hash_char(inp[i % len(inp)], key[i % len(key)])
return hashed
def hash_char(hash_char, key_char):
return chr(pow(ord(hash_char), ord(key_char), 26) + 65)this is related to jwt
The main weakness is in the modulo 26 operation (pow(..., ..., 26)). Since the modulus is very small, we can easily brute-force every character of the jwt_key
We have the “plaintext” (JWT data) and the “ciphertext” (signature) this allows us to launch a known-plaintext attack to find the key
def hash_char(hash_char, key_char):
try:
return chr(pow(ord(hash_char), ord(key_char), 26) + 65)
except (ValueError, TypeError):
return None
inp = "eyJhbGciOiAiQURNSU5IQVNIIiwgInR5cCI6ICJKV1QifQ.eyJ1c2VybmFtZSI6ICJhIiwgInBhc3N3b3JkIjogImEiLCAiYWRtaW4iOiAiZmFsc2UifQ"
known_signature = "JZOAYHBBBBNBDDQABXBFJOABZBLBBSOBVLBWVBQRSJJBOJYXDQZBEIRQBSOOFFWB"
cracked_key_chars = []
for i in range(64):
input_char = inp[i % len(inp)]
signature_char = known_signature[i]
found = False
for key_ord_candidate in range(256):
key_char_candidate = chr(key_ord_candidate)
if hash_char(input_char, key_char_candidate) == signature_char:
cracked_key_chars.append(key_char_candidate)
print(f"Position {i}: Input='{input_char}', Signature='{signature_char}' -> Found key character: '{key_char_candidate}' (ASCII: {key_ord_candidate})")
found = True
break
if not found:
print(f"FAILED at position {i}: No matching key character for input='{input_char}' and signature='{signature_char}'")
break
if len(cracked_key_chars) == 64:
print("".join(cracked_key_chars))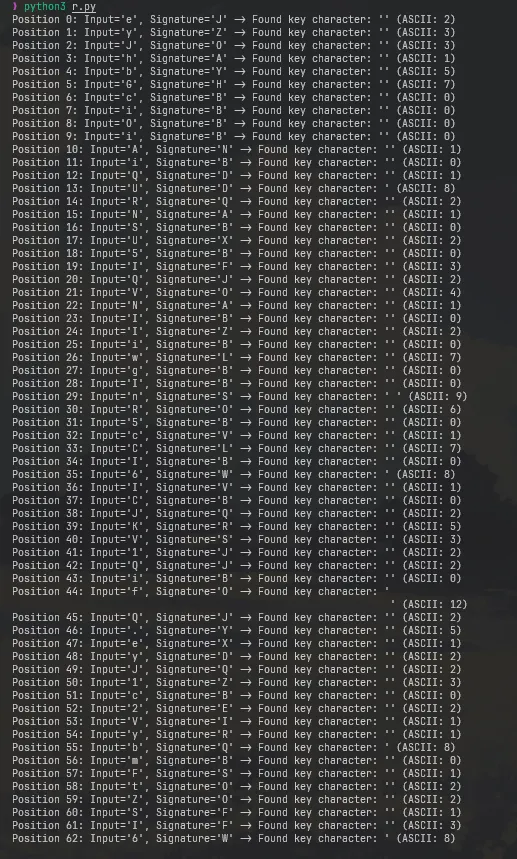
2, 3, 3, 1, 5, 7, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 8, 2, 1, 0, 2, 0, 3, 2, 4, 1, 0, 2, 0, 7, 0, 0, 9, 6, 0, 1, 7, 0, 8, 1, 0, 2, 5, 3, 2, 2, 0, 12, 2, 5, 1, 2, 2, 3, 0, 2, 1, 1, 8, 0, 1, 2, 2, 1, 3, 8, 0 is the key
then we can make a new JWT cookie,
def hash_char(hash_char, key_char):
return chr(pow(ord(hash_char), ord(key_char), 26) + 65)
def has(inp, key):
hashed = ""
for i in range(64):
hashed = hashed + hash_char(inp[i % len(inp)], key[i % len(key)])
return hashed
ascii_values = [2, 3, 3, 1, 5, 7, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 8, 2, 1, 0, 2, 0, 3, 2, 4, 1, 0, 2, 0, 7, 0, 0, 9, 6, 0, 1, 7, 0, 8, 1, 0, 2, 5, 3, 2, 2, 0, 12, 2, 5, 1, 2, 2, 3, 0, 2, 1, 1, 8, 0, 1, 2, 2, 1, 3, 8, 0]
jwt_key = "".join([chr(val) for val in ascii_values])
new_inp = "eyJhbGciOiAiQURNSU5IQVNIIiwgInR5cCI6ICJKV1QifQ.eyJ1c2VybmFtZSI6ICJhIiwgInBhc3N3b3JkIjogImEiLCAiYWRtaW4iOiAidHJ1ZSJ9"
new_signature = has(new_inp, jwt_key)
final_jwt = new_inp + "." + new_signature
print(final_jwt)output: eyJhbGciOiAiQURNSU5IQVNIIiwgInR5cCI6ICJKV1QifQ.eyJ1c2VybmFtZSI6ICJhIiwgInBhc3N3b3JkIjogImEiLCAiYWRtaW4iOiAidHJ1ZSJ9.JZOAYHBBBBNBDDQABXBFJOABZBLBBSOBVLBWVBQRSJJBOJYXDQZBEIRQBSOOFFWB
then set the new JWT,
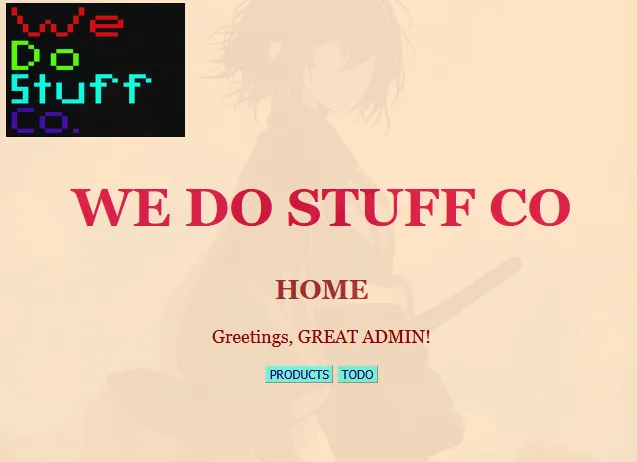
there is new endpoint /todo

first, i have no idea about what is this, so i just use dcode identifier, then i tried with XOR
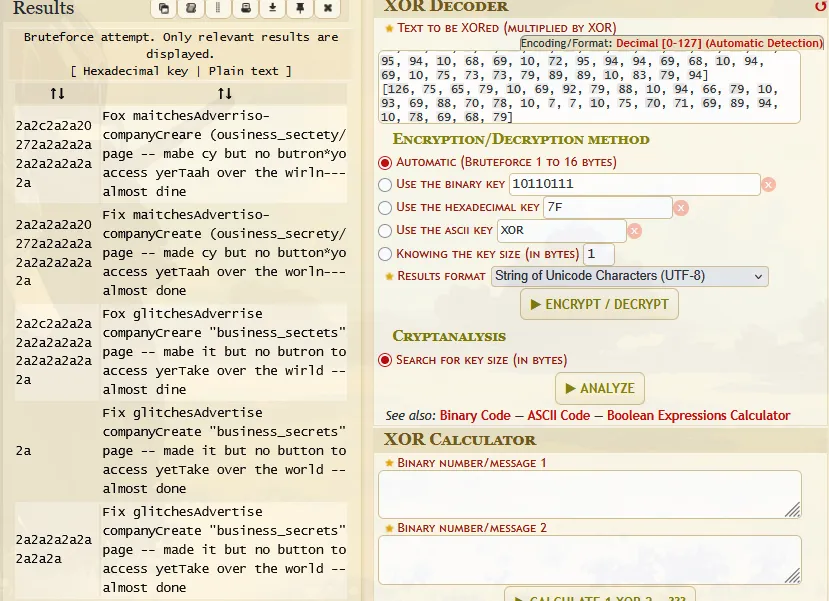
and access endpoint /business_secrets

tjctf{buy_h1gh_s3l1_l0w}